On this page
What Is HCM?
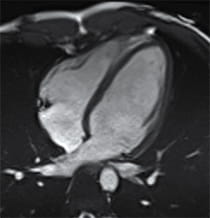
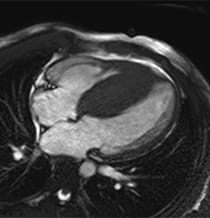
HCM is a genetic heart disease that causes the muscle fibers of the heart — mainly in the left ventricle — to thicken. It often affects the heart's ability to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
How common is HCM?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most common type of inherited heart disease in the U.S., affecting about 1 in 500 adults.
What are the types of HCM?
The septum — a wall of tissue inside the heart — divides the heart's left and right lower chambers.
In HCM, the heart muscle in the septum or elsewhere in the heart's left side thickens. This thickening may affect how blood flows.
There are two types of HCM:
- Obstructive HCM – A thickened septum changes how blood flows out of the heart to the body or how the heart's mitral valve opens or closes.
- Nonobstructive HCM – The left side of the heart thickens, and may become stiffer, affecting how well the heart circulates blood. The blood flow out of the heart doesn't change.
What causes HCM?
People with HCM often inherit the condition, meaning their parents passed the gene mutation to them. This mutation affects how the genes make the proteins that tell the heart muscle how to grow and how to contract to pump blood.
What are HCM risk factors and complications?
HCM risk factors
You might be at risk for HCM if someone in your family has the condition. But some people are the first in their family to have it.
Complications of HCM
Many people with genetic HCM don't have symptoms or are able to manage any symptoms they have. But HCM can cause complications, such as:
If you have HCM, it's crucial to routinely see your provider to track your condition.
Is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy a serious heart condition?
If left untreated, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can cause complications, including sudden cardiac death. It’s essential to see your provider if you have a family member who has been diagnosed with HCM. If you are diagnosed with HCM, it’s important to follow all treatment recommendations.
Back to top
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of HCM?
People with inherited HCM don't always have symptoms.
But some people have:
- Chest pain.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Heart palpitations or fluttery heartbeats.
- Trouble breathing.
Sometimes, people with HCM can die suddenly. HCM is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death in young people.
At what age does hypertrophic cardiomyopathy develop?
HCM can be diagnosed at any time, but the average age for diagnosis is around 39. Most people who develop HCM have a normal heart at birth and develop symptoms later in life.
When should I see a provider about my HCM symptoms?
If someone in your family has HCM, tell your provider. You might need to have a screening test to see if you have it, too.
If you have symptoms of HCM, schedule an appointment with your provider as soon as possible. If your symptoms are sudden and severe, dial 911 or visit the nearest hospital emergency room.
Back to top
How Do You Diagnose HCM?
If your family has a history of HCM or you feel symptoms, your provider will screen you for the condition.
What to expect during your visit
During your physical exam, your provider will:
- Ask about your symptoms and when they started.
- Discuss your medical history.
- Listen to your heart with a stethoscope.
Your provider may order further tests if they suspect you may have HCM or if you are having symptoms.
Tests to diagnose HCM
Providers use different tests to diagnose HCM, including:
- Cardiac MRI – A contrast agent is used with a magnet and radio waves to create an image of your heart. This imaging can better show your provider how thick your heart is and if there is any fibrosis or scarring that has occurred. This information can better guide your treatment plan.
- Echocardiogram – This test uses high-frequency sound waves to create an image of your heart.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) – Providers place patches on your skin. These patches connect through wires to a machine that measures your heart's electrical activity.
- Holter monitor – This at-home EKG tracks your heart for 24 to 48 hours, capturing data about how your heart is working.
Sometimes, providers order genetic testing for people with a family history of HCM. Using a blood sample, providers look for gene changes that cause the condition.
HCM prognosis
Early diagnosis and proper treatment of HCM can reduce your risk of developing life-threatening complications. Your provider will discuss your condition and prognosis with you.
What is the life expectancy of a person with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
Most patients with HCM have an average life expectancy. However, developing HCM at an earlier age is associated with more severe symptoms and an increased risk of complications.
What should you not do if you have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
People with HCM should follow their provider’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits, including:
- Avoiding heavy exercise or lifting heavy objects.
- Avoid smoking and illegal drugs.
- Avoid temperature extremes, including very hot or cold weather, hot tubs, and saunas.
Back to top
How Do You Treat HCM?
Your care team at UPMC will design an HCM treatment plan that's right for you.
Goals of HCM care are to:
- Educate you and your families about how to live with HCM.
- Improve your symptoms.
- Reduce potential complications.
Providers treat inherited HCM in several ways:
Lifestyle changes
When you have HCM, you should:
- Avoid strenuous exercise.
- Eat healthy foods low in saturated fats.
- Get routine mild to moderate exercise.
Medicine to treat HCM
Providers use drugs that help control blood flow and regulate heartbeats to manage HCM symptoms. These include:
- Antiarrhythmics.
- Beta-blockers.
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Water pills.
Surgery for HCM
Providers sometimes suggest surgery when HCM causes decreased blood flow. These procedures include:
- Alcohol septal ablation – Using a catheter, or thin tube, providers inject alcohol into a small artery that carries blood to the septum. Over time, the alcohol reduces the size of the muscle to allow blood to flow more freely.
-
Septal Myectomy – Myectomy is an open-heart surgery in which the surgeon trims the thickened muscle to allow blood to flow freely.
Sometimes people who have HCM surgery need an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). This is a small device placed in the chest to help regulate or stop dangerous heartbeats. UPMC is one of the only centers in the region that offers these surgeries to people with HCM.
How effective is treatment?
Your provider will work closely with you to develop an effective treatment plan that controls your symptoms and your risk of complications.
Back to top
Why Choose UPMC for HCM Care?
UPMC is one of the only centers in the region that offers a full range of surgical and nonsurgical treatment options for people with HCM. When you choose UPMC for your HCM care, you will benefit from:
- Care tailored to your unique needs – We will develop a comprehensive treatment plan to address your symptoms, goals, and preferences.
- The newest treatments based on research – These include clinical trials of new HCM drugs and new imaging techniques that help providers treat your disease.
- Access to advanced treatments and expertise – We're among only a few centers in the state to offer myectomy and alcohol septal ablation to treat the obstructive form of HCM.
By UPMC Editorial Staff.
Last reviewed on 2024-10-02 by Elissa Castor, PA-C.