Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is a tangled, enlarged mass of blood vessels that occurs due to abnormal connections between arteries and veins. AVMs don’t always cause symptoms, but they may bleed or rupture and can lead to stroke. They are most common in the brain and spine but can be found anywhere in the body.
On this page:
What Is Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
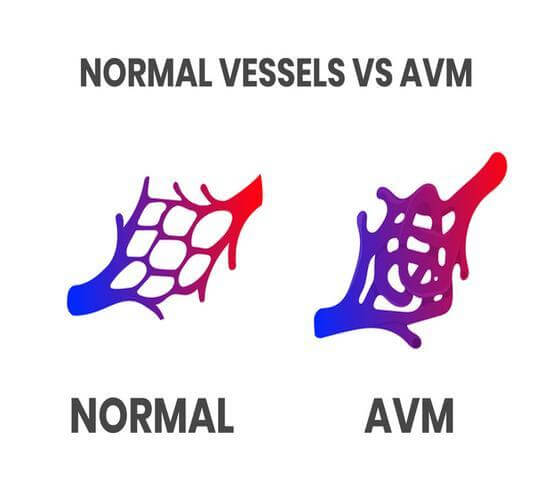
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are tangled, enlarged masses of blood vessels that occur because of abnormal connections between arteries and veins.
Arteries carry blood away from your heart, bringing oxygen and other nutrients to your organs and tissues. Blood then flows through very small vessels called capillaries into your veins, which bring the blood back to your heart.
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) occur when arteries and veins connect directly to each other rather than through capillaries. This creates tangled, enlarged masses of blood vessels and abnormal blood flow. Over time, this condition can cause tissue damage or nerve cell death.
AVMs can also grow larger over time. They are most common in the brain and spine, but can happen anywhere in the body where arteries and veins exist.
Most of the time, AVMs don’t cause any significant symptoms. Occasionally, AVMs may rupture and hemorrhage (bleed) into the brain. Hemorrhages can cause stroke or brain damage, which can lead to disability or death.
What are the types of Arteriovenous Malformation?
There are two types of AVMs:
- Brain arteriovenous malformations — Form in the brain, brainstem, and spinal cord, inside the brain tissue, or on the surface of the brain. Includes vein of Galen malformation, a severe type of AVM that forms deep inside the brain. It tends to co-occur with hydrocephalus (water on the brain) and can cause developmental issues or death.
- Peripheral arteriovenous malformations — Can form anywhere in your body.
How common is arteriovenous malformation?
AVMs are rare but can affect people of all races. AVMs are often congenital (present at birth) but typically are not genetic (passed down in families).
What causes arteriovenous malformation?
Although the cause of AVM is still unknown, there are a few theories. It is thought that they may be the result of blood vessel malformations during fetal development in the womb. They could also be the result of genetic mutations. It has also been observed that these lesions can be acquired as the result of an injury to the central nervous system.
Arteriovenous malformation risk factors
Risk factors for AVMs and AVM-related bleeding include:
- Age – Older people are at a higher risk of AVM hemorrhage.
- Family history – Though rare, AVMs may run in families; however, it is unknown if there's a genetic risk factor.
- Gender – Men are more likely to be born with AVMs.
- Hereditary conditions – Certain medical conditions, such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT), can increase the risk of AVMs.
- Previous bleed – A history of a prior bleed is a significant risk factor for AVM hemorrhage.
- Pregnancy – The risk of severe bleeding is higher during pregnancy due to increased blood volume and blood pressure.
Arteriovenous Malformation complications
AVMs can cause many complications, including:
- Abnormal sensations – AVMs can cause numbness, tingling, or spontaneous pain.
- Bleeding – AVMs have a high risk of bleeding, which can cause stroke and be fatal if left untreated.
- Brain or spinal cord compression – Large AVMs can grow up to 2.5 inches, pressing on the brain or spinal cord and causing neurological symptoms.
- Cognitive difficulties – AVMs can cause confusion, loss of function, and memory loss.
- Coordination problems – AVMs in the brain can cause loss of coordination.
- Dizziness – AVMs can cause dizziness if they damage the brainstem or cerebellum.
- Neurological problems – May occur as a result of a ruptured AVM.
- Seizures – Seizures are a complication of AVMs.
- Sleep disturbances, compromised hearing, or mental distress – AVMs can cause a bruit, or a rhythmic whooshing sound heard in an artery or vein. In severe cases, some people find this noise disruptive.
The most serious of these potential complications is bleeding (hemorrhage). Though the bleeding is not severe in most cases, it can sometimes be very serious and even fatal.
AVMs that are small or have bled once before are the most likely to cause bleeding. This bleeding can lead to bleeding elsewhere in the body, such as on the surface of the brain or spinal cord, reducing the amount of oxygen delivered to the brain or spinal cord.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Arteriovenous Malformation?
Most people with AVMs have no symptoms. In people with symptoms, the severity of the symptoms can vary depending on the location and size of the AVM.
Some AVM symptoms may include:
- Abnormal sensations, numbness, or tingling.
- Bruit (rhythmic, whooshing sound heard in an artery or vein).
- Cognitive difficulties or memory loss.
- Confusion or not being able to understand others.
- Developmental differences.
- Dizziness.
- Headache.
- Losing consciousness.
- Muscle weakness or paralysis.
- Numbness or weakness on one side of the body.
- Pain, especially of the back or lower limbs.
- Problems with speech, vision, or movement.
- Seizures.
- Vision loss.
Symptoms can appear at any age, but they are most often noticed in people over the age of 20, as AVM tends to occur from neurological damage that occurs over time. If a person reaches their late 40s or early 50s with no symptoms related to AVM, it is unlikely that symptoms will occur.
Symptoms may appear or worsen during pregnancy due to the increased blood volume and blood pressure.
When should I see a doctor about arteriovenous malformation?
You should see a doctor if you have any symptoms of AVM. If you notice symptoms of a brain AVM, such as seizures, headaches, or symptoms of a stroke, seek emergency medical care immediately.
How Do You Diagnose Arteriovenous Malformation?
Because most AVMs do not cause symptoms, doctors often diagnose an AVM while performing tests for another condition.
Tests that uncover an AVM may include:
- CT scans – A CT scan is a test that creates images of organs and structures in your body.
- MRI scans – MRI is a diagnostic procedure that combines large magnets, radio frequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within your body.
Tests to diagnose arteriovenous malformation
If your doctor suspects you have an AVM, they may perform an:
- Angiogram – An angiogram uses a catheter and special x-rays to find the location and severity of the AVM.
- MRA – MRA, or magnetic resonance angiography, records the pattern and speed of blood flow throughout the veins, brain, and spinal cord.
- TCD – TCD, or transcranial Doppler ultrasound, uses high-frequency sound waves to detect and measure the speed and extent of hemorrhage.
How Do You Treat Arteriovenous Malformation?
Treatment for AVMs varies based on:
- AVM size and location.
- Overall health.
- Risk of hemorrhage.
- Symptoms.
Long-term AVM treatments may include:
- Brain surgery – Brain surgery removes the AVM. To minimize the risk of damaging important tissue, this treatment is most often recommended for AVMs that are relatively small and located near or on the surface of the brain or spinal cord.
- Endovascular embolization – A minimally invasive, catheter-based procedure that safely blocks blood flow, damaging the AVM and causing it to close. This procedure is often done in tandem with surgery or radiosurgery.
- Radiosurgery – Uses a beam of radiation to damage the AVM and cause it to close. This procedure is often recommended for small AVMs that haven’t ruptured.
Endovascular embolization and radiosurgery are the least invasive procedures and are especially effective at treating AVMs that appear deep in the brain. However, the complete closure of the AVM can take many months to occur following these procedures.
Medicine may also be used to manage pain and other symptoms caused by AVMs; however, it cannot treat or cure AVM.
How effective is arteriovenous malformation treatment?
The prognosis for an AVM depends on several factors, including whether the AVM is discovered before or after bleeding.
The survival rate of a ruptured AVM is around 90%, although you may experience some neurological problems after the rupture.
Why Choose UPMC for Arteriovenous Malformation Care?
At UPMC, our surgeons are experts in treating AVMs. We diagnose and treat AVMs in all areas of the body using medicine, embolization, radiosurgery, or open surgery.
















